I. Global Overview: Tech and Supply Chain
Technology is vastly changing the supply chain landscape. For many years, the supply chain industry has had a pivotal impact on the growth of many other industries such as manufacturing and retail just to name a few. Today, it’s a huge task for supply chain managers to not only keep up with changing technologies but also find new ways to improve operational efficiency and make sure their processes run smoothly.
The fusion of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) is set to be a critical driving force behind the enhancement of efficiency and the optimization of supply chain management protocols. Furthermore, there will be an intensified focus on integrating sustainability principles and ethical concerns, propelled by the growing global awareness and consciousness surrounding sustainability.
Companies are becoming more aware of the importance of resilience and flexibility and the need to build strong and adaptable supply chain architectures. These frameworks ought to be able to withstand interruptions and proactively reduce risks. This calls for the application of cutting-edge technologies and strategic methods that not only guarantee the business continuity of corporate operations but also prove their efficacy in emergencies like the recent COVID-19 pandemic and related lockdowns.
But as an industry as a whole, how prepared is the sector to embrace these technological advancements?
II. Technological Maturity
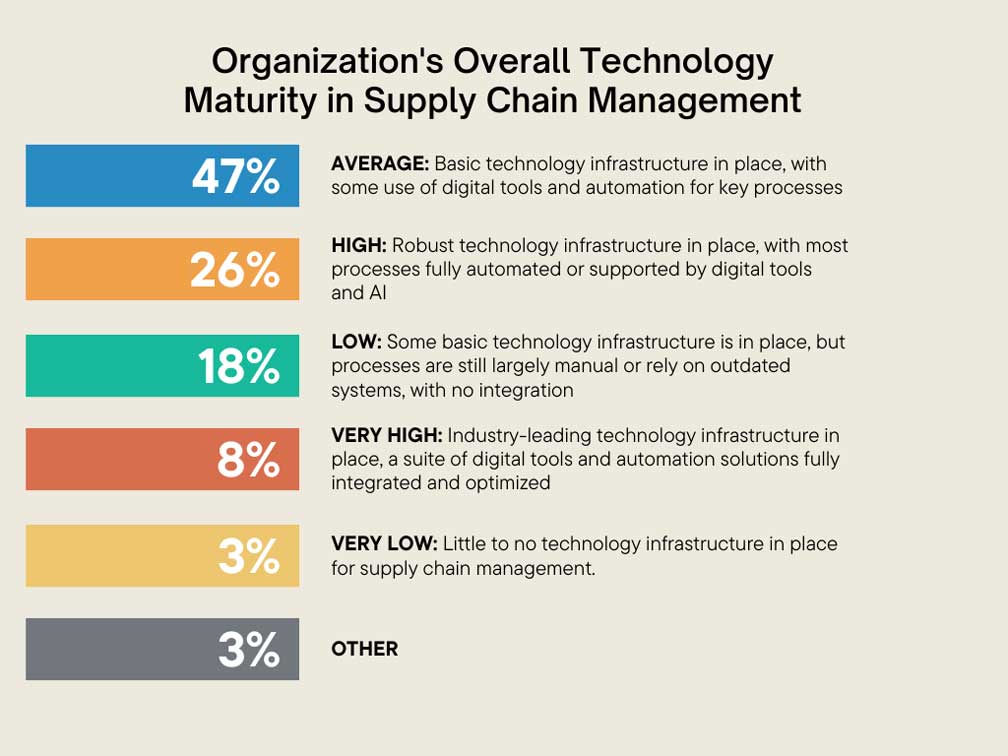
Earlier this year, Alcott Global conducted a survey involving the participation of over 300 supply chain executives. The study aims to map out the extent of technological maturity within the supply chain industry.
Among the respondents, a noteworthy 47% categorized their respective organizations as ‘Average’ in terms of level of technological maturity. This classification signifies that these organizations have at least established a foundational technological infrastructure and are actively leveraging digital tools and automation to streamline critical operational processes. In contrast, a mere 26% of the participants self-identified their organizations as being Technologically Mature.
Is average enough?
While more than the majority of the respondents are at the average/mature level in terms of technological maturity, the question arises: Is an ‘Average’ level of technological maturity enough for sustained success? While an ‘Average’ rating indicates the presence of essential technological underpinnings, along with the integration of select digital tools and automation, it might fall short in the context of today’s rapidly evolving business environment.
In an era characterized by perpetual transformation, meeting the baseline might not align with the demands of the competitive landscape. To effectively navigate industry advancements and meet the ever-heightening expectations of customers, organizations often aspire to ascend to higher tiers of technological maturity. This endeavor involves a proactive approach that entails investments in cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, comprehensive data analytics, the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain, among other innovations.
These advanced technologies not only bolster operational efficiency but also contribute to strategic decision-making and the development of value-added services. In essence, pursuing elevated technological maturity is a means to not only keep pace with industry trends but also to proactively shape them.
III. Technologies to Leverage On:
In the same study conducted by Alcott Global, supply executives have helped identify technological trends to focus on:
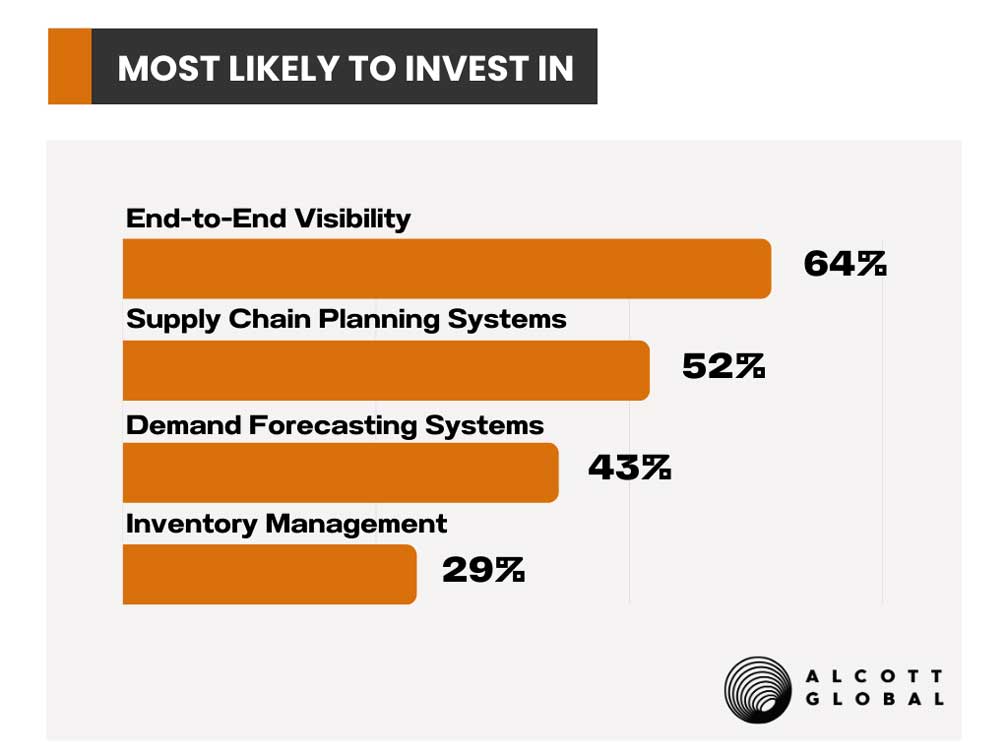
- End-to-End Visibility: A Strategic Imperative
The concept of end-to-end visibility in the supply chain holds immense strategic value for organizations. By encompassing a comprehensive view of all operational facets, this approach empowers businesses to identify bottlenecks, anticipate potential disruptions, and make well-informed decisions. This holistic comprehension not only paves the way for improved efficiency and cost reduction but also elevates the level of customer satisfaction. Moreover, such transparency fosters collaborative endeavors and streamlined communication amongst various stakeholders within the supply chain. This heightened cooperation translates into enhanced agility and responsiveness, enabling the prompt tackling of challenges and the fulfillment of customer requirements. - Supply Chain Planning Systems
Optimization through Supply Chain Planning Systems stands as an indispensable tool that leverages data analytics, modeling, and simulation techniques to optimize diverse processes. These include aligning demand and supply, optimizing production schedules, designing distribution networks, and planning transportation logistics. Through these technologies, organizations gain invaluable insights into resource allocation, lead times, capacity utilization, and overall supply chain performance. Armed with these insights, companies can make informed decisions grounded in data, resulting in increased productivity and the maintenance of customer satisfaction throughout the intricacies of supply chain operations. - Precision with Demand Forecasting Systems
The integration of demand forecasting systems equips companies with the capability to generate precise forecasts across various dimensions, such as specific Stock Keeping Units (SKUs), geographical regions, or customer segments. The refinement of forecast accuracy holds the potential to optimize inventory levels, minimize instances of stockouts, and mitigate excessive inventory. This refinement directly translates to enhanced responsiveness within the supply chain, a heightened quality of customer service, and the curbing of costs linked to inventory maintenance and management. - Elevating Efficiency through Inventory Management
The art of inventory management emerges as a cornerstone for maintaining equilibrium between customer demand and supply, all while minimizing costs and maximizing operational efficiency. The strategic investment in inventory management technology involves the adoption of systems that provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, streamline replenishment procedures, and empower effective control over inventory. By embracing these technologies, organizations unlock the potential for swift decision-making, the optimization of inventory-related processes, and the assurance of seamless operations within the supply chain framework.
IV. Trending Supply Chain Techs
1. Digital Freight Matching
The emergence of digital freight matching (DFM) platforms is revolutionizing the supply chain industry. These platforms connect shippers and carriers in real time, using advanced algorithms to enhance efficiency and responsiveness. This contrasts with the traditional method of relying on brokers, which led to delays and increased costs. DFM platforms offer transparency, automation, and optimization, benefiting both parties by efficiently matching cargo with suitable carriers.
2. Last Mile
The “last mile” of delivery, the final leg of the supply chain to the customer’s doorstep, is receiving increased attention due to e-commerce growth. Innovations like autonomous vehicles and drones, smart lockers, and route optimization software are addressing challenges in this segment. These technologies reduce costs, improve delivery speed, and offer sustainable alternatives. Improved analytics enhance route planning and customer communication, leading to better resource utilization and lower operational expenses.
3. AI and Machine Learning
Utilizing AI-driven solutions empowers businesses to enhance their entire supply chain process.
These technologies have the capability of predicting problems in advance and proactively prescribing solutions to manage such disruptions. They can also eliminate inefficiencies through intelligent automation and provide visibility and insights that enable effective decision-making and planning.
4. Visibility Platforms
Visibility platforms are transforming supply chain management by providing real-time insights. They track goods throughout the supply chain journey, enabling quick issue identification and resolution. With advanced analytics, they predict risks and trends, fostering proactive decision-making. Centralized communication platforms encourage collaboration among stakeholders, improving coordination and alignment.
The Internet of Things (IoT) and sensors play a critical role in supply chains. By providing real-time data collection and connectivity, they optimize operations, enhance visibility, and ensure product quality and safety. IoT devices monitor parameters like temperature and location, enabling quick responses to deviations. Integration with other systems offers a holistic view of the supply chain, enhancing decision-making and risk management.

6. Digital freight forwarding
Digital freight forwarding modernizes global shipping processes through online platforms. It automates booking, documentation, and tracking, simplifying complex logistical tasks. Transparency and visibility are increased, leading to informed decisions and efficient operations. Advanced technologies, like AI and machine learning, offer data-driven insights for cost-effective routing and risk identification.
Effective supply chain planning is crucial for modern businesses. Data-driven forecasting tools improve demand management, while integrated business planning (IBP) aligns supply chain decisions with overall strategies. Multi-product enterprises face challenges in managing diverse product portfolios and customer demands. They benefit from inventory optimization, end-to-end visibility platforms, and agile production strategies.
8. Supply Chain Agility
Future supply chains must be highly dynamic, anticipating and adapting to evolving demand and shifting product-channel combinations. Technologies that enable supply chain agility empower companies to effortlessly navigate change, seizing new business prospects amid fluctuating market conditions. This agility is underpinned by the extensive integration of digital technologies into operations.
Conclusion
The landscape of supply chain management is undergoing rapid transformation. The digital age has brought about a period characterized by increasingly intricate supply chains, where companies are adopting more global operational approaches and relying on data-driven strategies to maintain their competitiveness.
Supply chain management is a prime example of how technology can bring about improvements in operational efficiency, cost savings, and safety within supply chains. By strategically advancing technological maturity within supply chains, companies confer a competitive advantage by enhancing various aspects such as efficiency, visibility, responsiveness, risk management, collaboration, and sustainability. Organizations that enthusiastically adopt and harness advanced technologies are better poised to adjust to shifting market dynamics, provide exceptional customer experiences, and achieve lasting success.